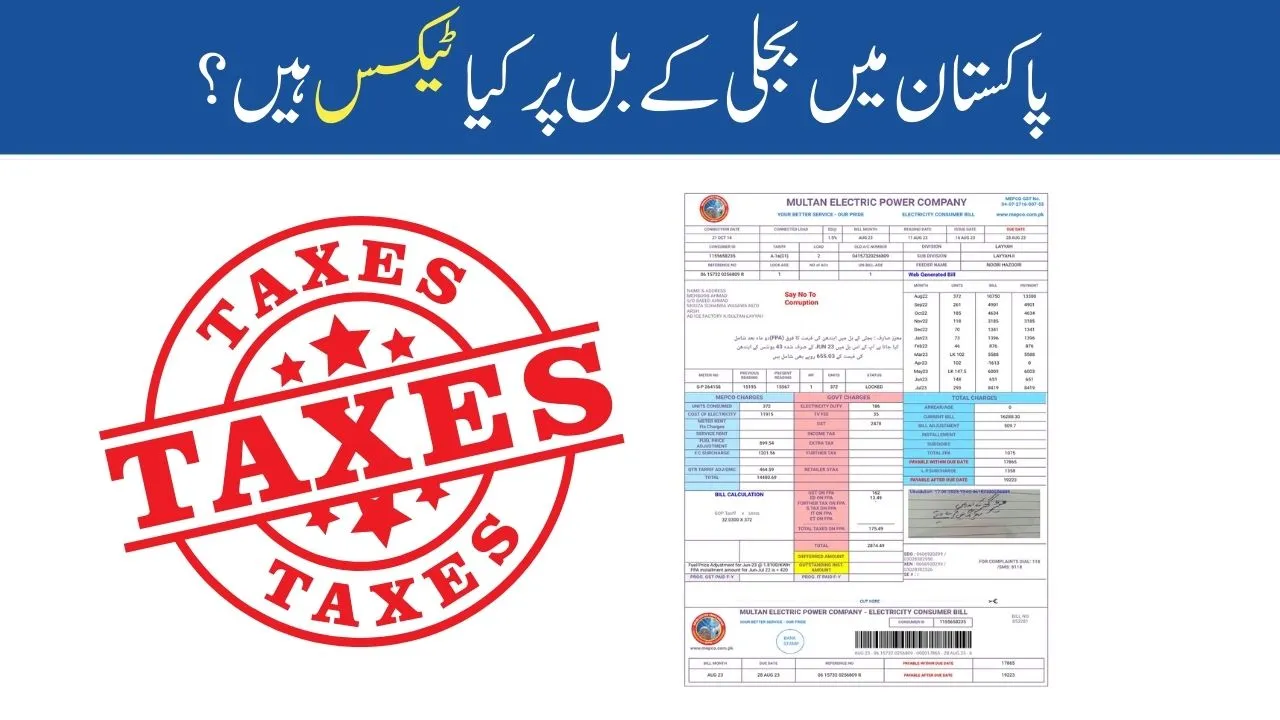
Electricity bills in Pakistan include different types of taxes in addition to the charges for the electricity used. These taxes are applied to cover various costs such as fuel price changes, infrastructure development, and late payment fees. Understanding these taxes can help you manage your electricity costs better.
| Tax | Description |
| FPA | Fuel Price Adjustment |
| TRS | Transmission and Distribution Surcharge |
| FCS | Finance Cost Surcharge |
| Deferred Amount | Late fee for paying after the due date |

Contents
What is FPA (Fuel Price Adjustment)?
FPA stands for Fuel Price Adjustment, which is added to your electricity bill when there is a change in the fuel cost used to generate electricity. If the actual fuel cost is higher than the benchmark cost, FPA is charged to cover the difference. If the fuel cost is lower, a credit may be given to consumers. FPA plays a significant role in increasing electricity bills when fuel prices rise.
Formula to calculate FPA:
FPA = (Actual cost of fuel – Benchmark cost of fuel) × Total units consumed.
For example, if the actual fuel cost is Rs. 10 per unit the benchmark cost is Rs. 8, and you consumed 100 units, the FPA will be:
(10 – 8) × 100 = Rs. 200
Also Read: Zong 4G Partners with MEPCO for Better Business Communication
TRS Surcharge (Transmission and Distribution)
TRS stands for Transmission and Distribution Surcharge. It’s a tax that helps improve and modernize the electricity infrastructure in certain areas. This surcharge is added to your bill to cover the cost of maintaining and upgrading the distribution network.
Formula to calculate TRS:
TRS = Total cost of infrastructure / Total electricity consumed.
For instance, if the infrastructure cost is Rs. 100,000 and you used 1000 units, the TRS would be:
100,000 / 1000 = Rs. 100 per unit.
FCS (Finance Cost Surcharge)
The Finance Cost Surcharge (FCS) is another tax applied to electricity bills to cover the cost of borrowing money for infrastructure projects. The cost of these loans is spread across the total units of electricity consumed by users in a particular area.
Formula to calculate FCS:
FCS = Total cost of borrowing / Total electricity consumed.
If the cost of borrowing is Rs. 100,000 and you used 1000 units, the FCS would be:
100,000 / 1000 = Rs. 100 per unit.
- FPA is based on fuel price changes.
- TRS helps improve infrastructure.
- FCS covers the cost of borrowing for projects.
- Pay your bill on time to avoid deferred charges.
Deferred Amount (Late Fee)
The deferred amount is charged when a customer does not pay their electricity bill by the due date. This amount is basically a late fee, and it encourages customers to pay their bills on time. The longer the delay in payment, the higher the deferred amount becomes.
Calculation of Deferred Amount:
The deferred amount is calculated by multiplying the number of days delayed with the daily deferred charges. For example, if the due date was January 10 and you paid on January 19 (9 days late), and the daily deferred charge is 2%, the deferred amount will be:
Deferred Amount = 9 days × 2% × total bill.
ATR Tariff (Average Transmission and Distribution Tariff)
The ATR Tariff is applied to cover the cost of transmitting and distributing electricity to homes. This fee helps maintain and improve the grid.
Formula to calculate ATR:
ATR = Total cost of infrastructure / Total electricity consumed.
For example, if the infrastructure cost is Rs. 100,000 and you used 1000 units, the ATR tariff would be:
100,000 / 1000 = Rs. 100 per unit.
Also Read: MEPCO Announces Power Shutdown Schedule 2024
Conclusion
Understanding the different taxes and surcharges on your electricity bill can help you plan better and avoid extra charges. Paying your bill on time and managing your energy usage efficiently are important steps to lower your costs.
FAQs
How can I calculate the FPA on my bill?
You can calculate the FPA by subtracting the benchmark fuel cost from the actual cost and multiplying it by the total units consumed.
What happens if I pay my bill late?
If you pay your bill late, a deferred amount or late fee will be added to your bill based on the number of days delayed.
What is the purpose of the TRS surcharge?
The TRS surcharge is used to upgrade and maintain the electricity distribution network in specific areas.